Description:
The current state of the art:
Despite the advancement in immunotherapy and other targeted therapy for the treatment of cancer, the success rate remains low in solid tumors. Targeting the tumor microenvironment (TME) is a new promising treatment strategy. Infiltrated in TME, tumor-associated macrophages, especially CD206 positive M2 macrophages, play a pivotal role in tumor development and metastasis, especially in breast cancer. As a result, removing CD206 positive M2 macrophage can be a promising therapeutic candidate.
The problems with the current art:
An effective drug delivery system that has higher specificity to the M2 macrophage and to accumulate in the tumor is needed. Exosome, a biocompatible delivery system has shown promising results as novel therapeutic vehicles in cancer immunotherapy. However, the exosome system that targeting both M2 macrophage and effectively inhibit tumor growth is lacking.
The advantages of our invention:
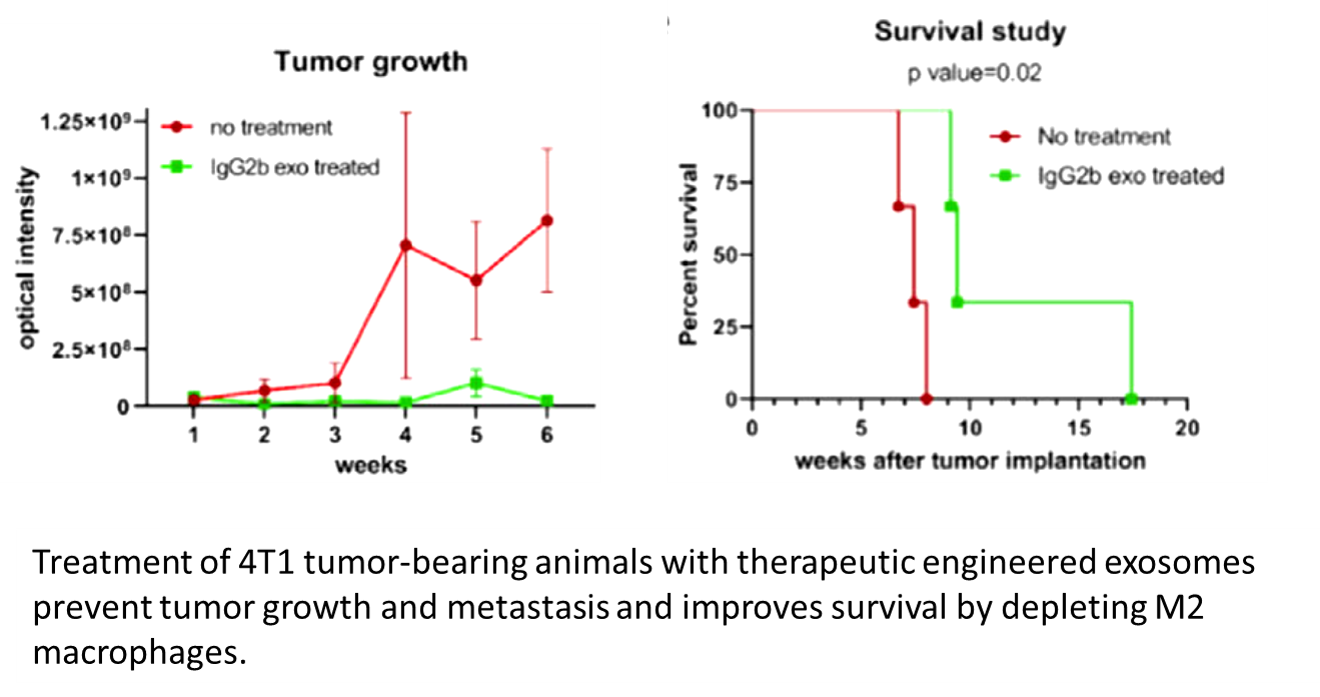
Scientists at AU developed a novel engineered exosome delivery system expressing the CD206 binding peptide which binds to CD206 positive M2 macrophage and Fc portion of mouse IgG2 which binds to the Fc receptor on effector cells to induce the antigen-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of CD206+ M2 macrophages. In cell culture and animal studies, scientists have shown the delivery of these engineered exosomes can detect the distribution of CD206+ M2 macrophages, induce cell death, and inhibit tumor growth. Therefore these engineered exosomes with CD206 binding peptide and Fc portion of the receptor can be a promising platform for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
AURI-2019-029
Lead Inventor: Ali Arbab, https://www.augusta.edu/cancer/research/labs/ali-arbab.php
IP status: 62/926,775 (filing date: 10/28/2019)
Reference: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/adtp.201900209